What Is an Advantage of Mild Inflation According to Some Economists?
Readers Question: what are the advantages and disadvantages of inflation?
Inflation occurs when there is a sustained increase in the full general cost level. Traditionally high aggrandizement rates are considered to be damaging to an economic system. High aggrandizement creates incertitude and can wipe away the value of savings. However, nigh Central Banks target an aggrandizement rate of 2%, suggesting that low inflation can have various advantages to the economy. Some economists even argue we should target a higher inflation charge per unit during periods of economic stagnation.
The advantages of aggrandizement
ane. Deflation (a fall in prices – negative inflation) is very harmful. When prices are falling, people are reluctant to spend money considering they feel that appurtenances will be cheaper in the future; therefore they go along delaying purchases. Besides, deflation increases the real value of debt and reduces the disposable income of individuals who are struggling to pay off their debt. When people take on a debt like a mortgage, they generally look an inflation rate of 2% to help erode the value of debt over time. If this inflation charge per unit of 2% fails to materialise, their debt brunt will exist greater than expected. Periods of deflation caused serious problems for the UK in 1920s, Nihon in 1990s and 2000s and Eurozone in 2010s.
See more than Costs of deflation
two. Moderate aggrandizement enables aligning of wages. Information technology is argued a moderate charge per unit of inflation makes it easier to arrange relative wages. For example, it may be hard to cut nominal wages (workers resent and resist a nominal wage cut). Simply, if average wages are rising due to moderate aggrandizement, information technology is easier to increase the wages of productive workers; unproductive workers can accept their wages frozen – which is effectively a real wage cut. If we had naught inflation, we could end up with more real wage unemployment, with firms unable to cut wages to concenter workers.
3. Inflation enables adjustment of relative prices. Similar to the last indicate, moderate aggrandizement makes it easier to adjust relative prices. This is particularly of import for a single currency like the Eurozone. Southern European countries like Italy, Spain and Greece became uncompetitive, leading to large current account arrears. Considering Espana and Greece cannot cheapen in the Single Currency, they have to cut relative prices to regain competitiveness. With very low inflation in Europe, this means they accept to cut prices and cutting wages which cause lower growth (due to the furnishings of deflation). If the Eurozone had moderate inflation, it would be easier for southern Europe to adjust and regain competitive without resorting to deflation.
iv. Inflation can heave growth. At times of very low aggrandizement, the economy may be stuck in a recession. Arguably targeting a higher rate of inflation can enable a boost in economic growth. This view is controversial. Non all economists would support targeting a higher inflation rate. Still, some would target higher inflation, if the economy was stuck in a prolonged recession. See: Optimal aggrandizement rate
For case, the Eurozone has had a very low inflation charge per unit in 2013-fourteen, and this has corresponded to very weak economic growth and very high unemployment. If the ECB had been willing to target college aggrandizement, and so we could have seen a ascension in Eurozone GDP.
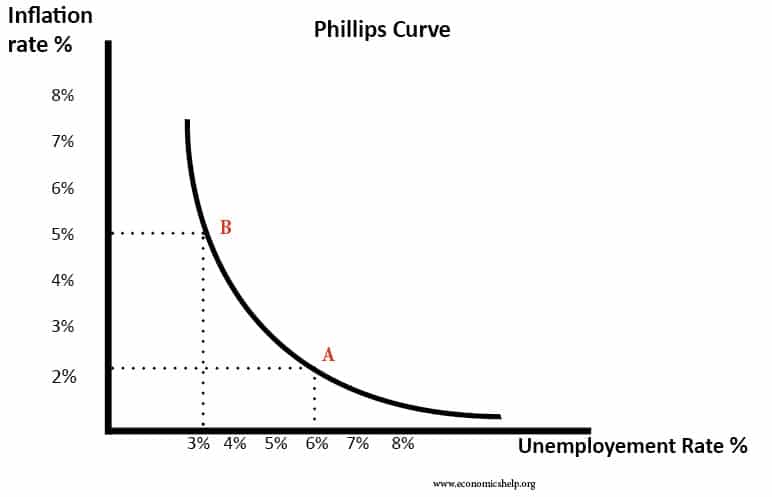
The Phillips Curve suggests there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. Higher inflation leads to lower unemployment (at least in the short-term) there is a debate most how meaningful this trade off is.
5. Inflation is improve than deflation. The only affair worse than inflation, joke economists, is deflation. A autumn in prices tin can crusade an increment in the real debt burden and discourage spending and investment. Deflation was a gene in the Great Low of the 1930s..
Disadvantages of inflation
Aggrandizement is usually considered to be a problem when the inflation charge per unit rises above 2%. The higher the inflation, the more serious the problem is. In extreme circumstances, hyperinflation tin wipe away people's savings and crusade great instability, e.g. Deutschland 1920s, Republic of hungary 1940s, Republic of zimbabwe 2000s. However, in a modern economy, this kind of hyperinflation is rare. Commonly, inflation is accompanied with higher interest rates, so savers do not see their savings wiped away. However, inflation tin still cause problems.
- Inflationary growth tends to exist unsustainable leading to a damaging period of blast and bust economic cycles. For example, the Great britain saw loftier inflation in the late 1980s, but this economic boom was unsustainable, and when the government tried to reduce inflation, it led to the recession of 1990-92.
- Inflation tends to discourage investment and long-term economic growth. This is because of the incertitude and defoliation that is more likely to occur during periods of high inflation. Low inflation is said to encourage greater stability and encourage firms to accept risks and invest.
- Inflation can make an economy uncompetitive. For example, a relatively college rate of aggrandizement in Italian republic can make Italian exports uncompetitive, leading to lower Ad, a electric current account arrears and lower economic growth. This is particularly important for countries in the Euro-zone because they can't cheapen to restore competitiveness.
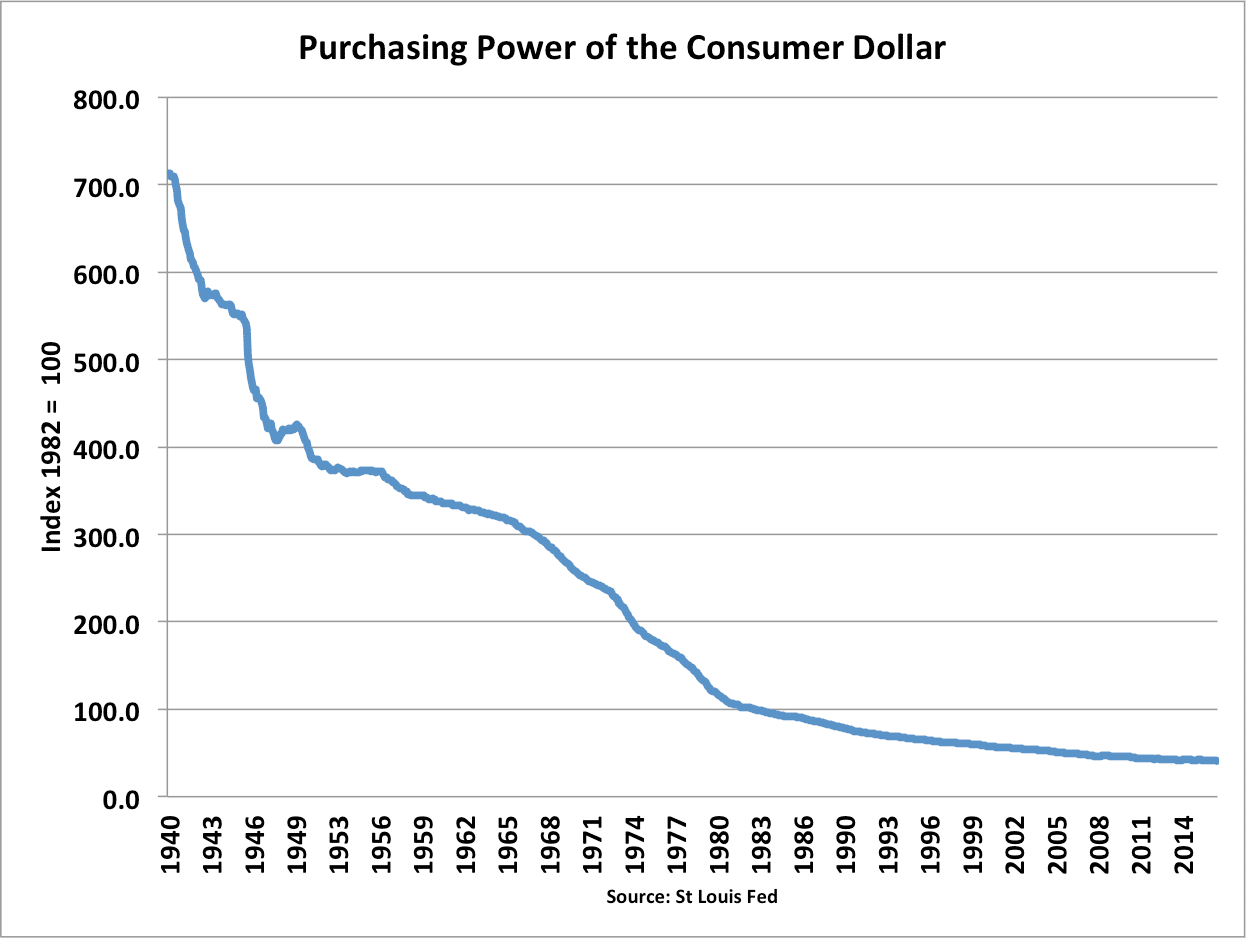
- Reduce the value of savings. Inflation leads to a autumn in the value of money. This makes savers worse off – if aggrandizement is college than interest rates. High aggrandizement tin can lead to a redistribution of income in order. Often it is pensioners who lose out well-nigh from aggrandizement. This is particularly a trouble if inflation is high and interest rates low.
- Menu costs – the price of changing prices lists becomes more frequent during high inflation. Not so significant with modern engineering.
- Fall in real wages. In some circumstances, loftier inflation can pb to a autumn in real wages. If inflation is higher than nominal wages, then real incomes autumn. This was a problem in the dandy recession of 2008-16, with prices rising faster than incomes.
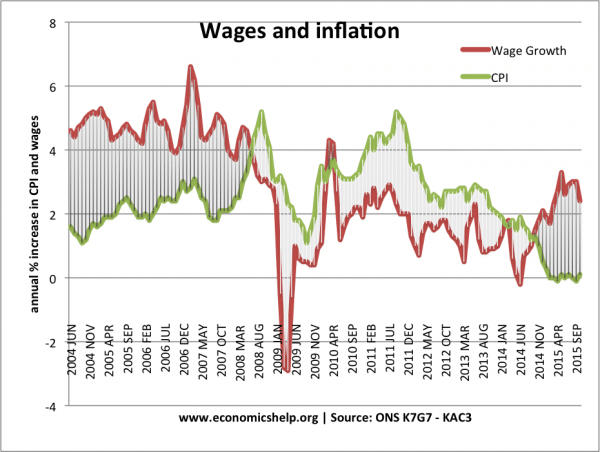
Inflation (CPI) above wage growth 2008-14, caused a decline in living standards – particularly for workers in low-wage, zero-hour contract jobs.
Related
- Is Inflation benign?
- Costs of Inflation
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/315/inflation/inflation-advantages-and-disadvantages/
0 Response to "What Is an Advantage of Mild Inflation According to Some Economists?"
Post a Comment